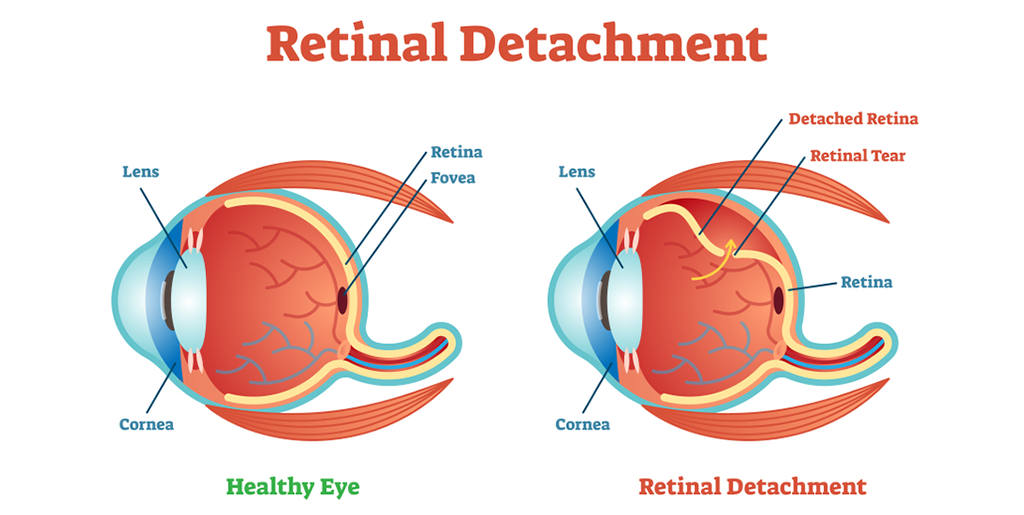
Seeing things clearly is not possible without a healthy retina, which comprises of a thin layer of light-sensitive cells present at the back of the eye, held in place by an underlying layer of support tissues. When retina is peeled away or detaches from this underlying support, the phenomenon is referred as ‘retinal detachment’.
Usually, retinal detachment takes place only in one eye, and should be considered and treated as a severe medical emergency.
Initially, only a small area of the retina might get affected by the detachment, but delaying the treatment might lead the whole of retina to peel off, which will inflict vision loss permanently.
People suffering from diabetes, severe form of myopia (farsightedness), cataract surgery complications, or someone receiving severe concussion or a blow to the eye are highly susceptible to this vision threatening eye condition.
What Are Some Signs and Symptoms of Retinal Detachment
It is not usually a painful condition, but different types of retinal detachment symptoms might be observed. Some of them include:
Are There Different Types of Retinal Detachment?
Yes, there are three types of retinal detachment:
Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment:
It refers either to a hole, tear or break in the retina, which creates a passage for the liquid in the vitreous space to the subretinal space existing between the sensory retina and the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) – a pigmented cell layer covering the neurosensory retina.
Secondary Retinal Detachment:
This type of detached retina is also named as serous retinal detachment and exudative retinal detachment. It happens as a result of fluid build-up under the retina due to an injury, inflammation or vascular abnormalities and there is no tear, break or whole involved.
Tractional Retinal Detachment:
When fibrovascular tissue pulls the sensory retina from the retinal pigment epithelium due to an injury, inflammation or neovascularization, the phenomenon is referred as ‘tractional retinal detachment’.
What Causes Retinal Detachment?
There’s a layer of light-sensitive tissues lining the inside of the eye, which also serves to send visual signals to the brain using optic nerve as the medium. Pulling up of this layer from its original position is referred as ‘retinal detachment’. Sometimes, retina encounters small tears, which can also lead to retinal detachment.
Retinal Detachment Diagnosis
In case of suspicion of a detached retina, a doctor will immediately refer you to an eye doctor or ophthalmologist for detailed examination, who will run through a thorough examination of the suspected eye. Sometimes, an ultrasound is also helpful in the process of diagnosing the condition correctly.
Retinal Detachment Treatment Options
Surgery serves as the best way of treating retinal detachment, through which eye doctors identify and seal different types of retinal detachments and there’s a high risk of total vision loss if you delay surgical treatment.
Various options for retinal detachment surgery include:
Laser Surgery for Retinal Detachment or Photocoagulation:
Eye doctors user a laser beam for this type of treatment, which is directed at the tear in the retinal tissue through a contact lens or ophthalmoscope. This results in burning around the retinal tear, which produces scar tissue, which fuses back the tissue together later on.
Cryotherapy:
In fact, this type of surgery is referred to by different names, i.e. cryopexy, cryosurgery or freezing, which involves application of extreme cold for destroying abnormal or diseased tissues in the retina. A delicate scar is produced as a result of the surgery, which helps retina connect to the wall of the eye.
Scleral Buckling:
In this innovative treatment of retinal detachment, ophthalmologists resort to very thin bands of silicone, which are sewn onto the sclera, the exterior white of the eye. Alternatively, rubber sponge can also be used for this purpose. The tissues around the area can either be frozen to produce the healing scar tissue or lasers can be used for the purpose.
Vitrectomy:
This procedure involves removing the vitreous gel from the eye and using a silicon oil bubble or gas bubble to hold the retina in place. The wound needs to be stitched after the procedure and the silicone oil needs to be extracted anywhere between 2-8 months of the procedure.
Pneumatic Retinopexy:
This type of surgery can be used to treat a detached retina in case of uncomplicated detachment. First, the tear area is frozen by using cryopexy, followed by injecting of a bubble into the vitreous cavity of the eye. As a result, retina is pushed back against the torn and detached area, preventing the flow of any fluid from behind the retina
The applied pressure eventually leads the retina to reattach to the wall at the back of the eye, thus fixing the detachment.
Not very common, but complications after a surgery for detached retina are quite possible; for instance, eye infection, allergic reaction to medication, bleeding in the eye, cataracts, double vision and glaucoma.
Risk Factors for Retinal Detachment
There are a host of risk factors capable of increasing the probability of a person to get their retina detached. Some of them include:
Observing any of these risk factors, one should immediately consult an eye doctor for thorough eye examination, so that diagnosing and treating the issue in time can lead to best outcomes.