The fusion of the healthcare sector with technology can become confusing for the general public due to the technicalities involved in both sectors. But innovations in the healthcare space have been picking pace and have become popular each day intending to increase the access to basic healthcare for patients, making healthcare management smoother for clinicians as well as improve the efficiency of service delivery in the healthcare domain.
The integration of healthcare service delivery into efficient technological mechanics can also be termed as “telematics.”
According to World Health Organization, “Health Telematics can be defined as a composite term for telemedicine, telehealth, or any health-related activity carried out over distance employing information communication technologies.”
Brief History of Telehealth and Telemedicine
Mordor Intelligence in its survey states that global IT healthcare is expected to reach $20 billion by 2020. So how and when did technology find its way into healthcare?
Well, as literature shows, telehealth roots back to the 18th century as reported by the National Center for Biotechnology Information. There are 2 prominent examples of the early adoption of telehealth:
- Discussion on the possibility of using the telephone to reduce unnecessary office visits as reported in the Lancet article in 1879
- A magazine displayed a doctor diagnosing a patient by radio, while also pointing out the potential of using a device that would enable video examination of a patient over a distance.
As for Telemedicine earliest foundations can be traced back to Europe, when a Dutch physician by the name of Willem Einthoven, utilized long-distance transfer of electrocardiograms dated as early as 1905 whereas the first wave of organized telemedicine programs in the United States began in the late 1950s as reported by National Center for Biotechnology Information.
What Is Telemedicine?
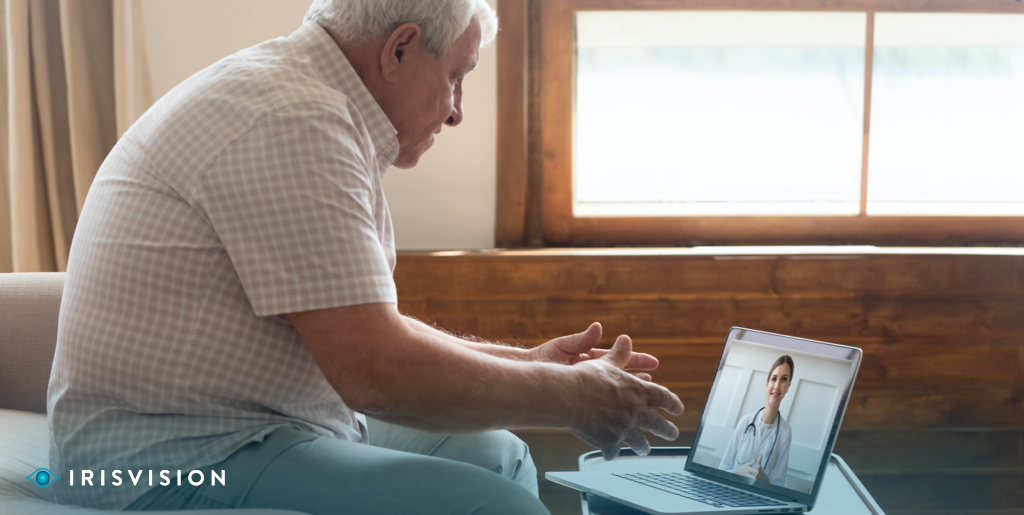
Telemedicine can be defined as a process that integrates the practice of medicine using communication or information technology to deliver remote care. This requires the use of electronic communications and its relevant technological components to facilitate patients with clinical services as well as assist clinicians to remotely monitor the patient, altogether withdrawing the need for an in-person visit.
The current pandemic outbreak has shown a clear rise in the adoption of Telemedicine technology and its offerings. With telemedicine, follow-up visits, management of chronic conditions, medication management, and specialist consultation can be provided remotely.
In the contemporary world, the global health care system is changing much through the application of innovation. Technology through telemedicine has allowed high-quality healthcare service delivery to reach the most remote and rural areas. Though the challenges attached with this healthcare model may seem greater, the benefits overweigh in many aspects. The benefits of telemedicine are far-reaching as it offers approaches for centralizing specialists, reducing costs, supporting primary care clinicians.
The adoption of telemedicine worldwide means, equipping human civilizations to adapt better to public health emergencies such as Covid-19, which requires rapid deployment of large numbers of healthcare providers and providing basic healthcare services that local hospitals and healthcare centers are unable to deliver. Telemedicine is a means of providing healthcare information to infected people and also non-infected people, which is why it is important to shift the discussion from the use of telemedicine for public health emergencies to chronic conditions management to include diabetic, heart, or other areas of healthcare service provision. This requires increased discussions as well as the integration of telemedicine into accreditation for healthcare providers, funding, and redesigning clinical care models among other things. It is safe to say that as communications technology advances and progresses, the quality of healthcare service delivery will improve due to correlation between the two domains.
As a result of the progress made in information technology and the increased demand for such innovations, new methods have emerged such as automated logic flows – their unique property is to identify moderate and high-risk patients and direct them to triage lines with nurses on board, enabling you to also benefit from video visits to avoid in-person interaction as reported in National Institute of Health.
What Is Telehealth?
Telehealth can be defined as a subset of e-health and covers a broader scope of integration of electronic and telecommunications technologies with healthcare service delivery.
While telemedicine is termed as an extension of telehealth, the main differentiating factor is that telemedicine refers to remote clinical services whereas telehealth also encompasses remote non-clinical services, e.g. service provider training, administrative meetings, medical education, etc. According to the World Health Organization, telehealth includes services provided by health professionals in general, including nurses, pharmacists, and others.
Telehealth takes into account most disciplines related to the healthcare sector such as psychiatry, dentistry, cardiology, etc. With numerous benefits for clinicians and patients, remote access to basic healthcare services can be used as an effective tool to cater to the socially marginalized segment (medically or socially vulnerable) providing an alternate solution when an in-person visit is not doable. In matters of a medical emergency or requirement of urgent care, telehealth is a way through which medical consultation or assessment can be provided efficiently. Patients previously undergone surgeries or hospitalized can receive regular counseling or training such as instructing patients regarding physiotherapy post-surgery. It guarantees access to primary care providers and specialists, ranging from chronic health conditions, medication management, weight management, nutrition counseling, etc.
What is the Difference between Telehealth and Telemedicine?

Telehealth’s primary differentiating factor is that it refers to a broader scope of remote health care services than telemedicine. Telemedicine ]categorizes as remote clinical services, whereas telehealth also takes into account non-clinical services.
Examples of telemedicine include the use of sharing medical details between the service provider and the patient whereas telehealth includes education for medical professionals and general administrative practice etc.
Some of the popular examples of telemedicine are:
Whereas Telehealth is inclusive of:
Though components of telemedicine and telehealth may differ, both support the broader goal of making remote clinical services accessible, turn health management for patients efficiently, and improve the efficiency of the overall healthcare delivery system. Though licenses and other regulatory policies may vary by state, service providers are investing their efforts to address sensitive topics like patient discomfort or privacy concerns.